VEM : VAPS®-EPSCON-MKJ
5.6K subscribers
About VEM : VAPS®-EPSCON-MKJ
*Your One-Stop Solution for Finance, Education, and Career Growth* - *Regular Updates*: Stay informed about the latest developments in finance and accounts. - *Invaluable Tips and Guidance*: Expert advice to help you navigate the world of finance. - *Education and Training*: Enhance your knowledge and skills through comprehensive programs. - *Job Opportunities*: Explore career options in finance-related industries.. - *Health and Fitness*: Get updates and tips on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and achieving fitness goals. *Stay Connected*
Similar Channels
Swipe to see more
Posts

*The Power of Daytime Sleep: Why You Should Catch Some Z's* Sleeping during the day can be a game-changer for your overall well-being. By incorporating a daytime snooze into your routine, you can: - *Prevent Burnout*: Daytime sleep helps prevent physical and mental exhaustion, reducing the risk of burnout and increasing productivity. - *Restore Your Body*: A short nap can recharge your batteries, improving cognitive function, memory, and creativity. - *Reduce Stress*: Daytime sleep can help regulate stress hormones, promoting relaxation and calmness. - *Rethink and Reflect*: A nap can give you a fresh perspective, allowing you to approach problems with a clear mind and new insights. *The Heart Health Benefits* Research suggests that regular daytime sleep can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that: - *Reduced Risk of Heart Disease*: Sleeping in the afternoon at least 3 times a week can lower the risk of heart disease by 40%. - *Protection Against Myocardial Infarction*: Daytime sleep is considered a powerful tool in preventing heart attacks and promoting overall heart health. *Make Daytime Sleep a Priority* By prioritizing daytime sleep, you can: - Improve your overall well-being - Boost your productivity and creativity - Reduce stress and anxiety - Support your heart health So, take a cue from the science and give daytime sleep a try. Your body – and mind – will thank you!

*Boost Your Day with Lemon Water* Kick-start your morning with a refreshing glass of lemon water! This simple yet powerful habit offers numerous benefits, including: - *Liver Health*: Lemon water supports liver function and promotes detoxification by stimulating the liver to produce more bile, which helps remove toxins from the body. - *Blood Sugar Stabilization*: It helps regulate blood sugar levels, keeping you energized throughout the day by slowing down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. - *Metabolism Boost*: Lemon water naturally kick-starts your metabolism, aiding in weight management and overall well-being by increasing your body's ability to burn fat and calories. *Additional Benefits* In addition to the benefits mentioned above, lemon water also: - *Supports Digestive Health*: Lemon water stimulates digestive enzymes, which helps improve digestion and reduce symptoms of indigestion and bloating. - *Hydrates the Body*: Drinking lemon water first thing in the morning helps rehydrate the body after a night of sleep, flushing out toxins and supporting overall health. - *Boosts Immune System*: Lemons are high in vitamin C, which plays a crucial role in immune function and can help fight off infections and diseases. *How to Make Lemon Water* Making lemon water is easy! Here's a simple recipe: - Squeeze the juice of 1/2 lemon into a glass of warm or room temperature water. - Stir well and drink immediately. - You can also add a slice of lemon to the water for extra flavor and nutrition. *Tips and Variations* - Use fresh lemons instead of bottled lemon juice for maximum benefits. - Adjust the amount of lemon juice to your taste. - Add a pinch of salt or honey to enhance the flavor. - Try drinking lemon water at different temperatures, such as cold or hot, to see what works best for you. *Make it a Habit* Incorporate this easy habit into your daily routine and experience the positive impact on your health and energy levels. Start your day off right with a glass of lemon water and set yourself up for success!

*Job Opportunity: Assistant Manager in Transfer Pricing at Deloitte, Bangalore* Deloitte is hiring CA freshers for the role of Assistant Manager in their Transfer Pricing team at their Bangalore office. If you're interested in this opportunity, you can apply by sharing your updated CV with Abhishek Tiwari at [email protected]. *Job Details:* - *Role*: Assistant Manager - *Team*: Transfer Pricing - *Location*: Bangalore - *Experience*: Freshers (CA qualified) *How to Apply:* If you're a CA qualified professional looking for a challenging role in transfer pricing, send your updated CV to [email protected]. *About Deloitte:* Deloitte is a leading global professional services firm providing audit, tax, consulting, and financial advisory services. With a strong presence in India, Deloitte offers a range of opportunities for professionals to grow and develop their careers.

The recent Air India plane crash in Ahmedabad resulted in a total of 279 deaths, including 241 passengers and crew members on board, and 38 people on the ground. The flight, a Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner, crashed shortly after takeoff from Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport, killing everyone except for one survivor, Vishwash Kumar Ramesh. Here's a breakdown of the casualties : - *On-board fatalities*: 241 passengers and crew members - *Ground fatalities*: 38 people, including medical students, doctors, and residents in the nearby area - *Total fatalities*: 279 people The incident has sparked an investigation, with the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) recovering the flight data recorder (black box) to determine the cause of the crash. Possible causes being considered include dual engine thrust loss, bird strike, pilot error, or technical fault .

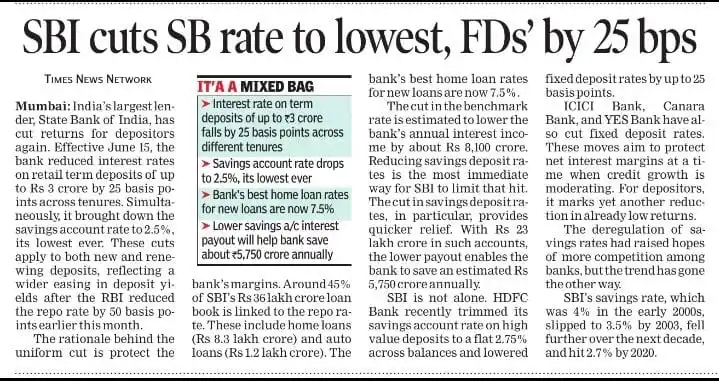
SBI has indeed reduced its interest rates on retail term deposits by 25 basis points and cut its savings account rate to a historic low of 2.5%. Here's what you need to know : - *Savings Account Rate*: The new savings account rate of 2.5% per annum applies to all savings account balances, down from 2.7% for balances below Rs 10 crore and 3% for balances of Rs 10 crore and above. - *Fixed Deposit Rates*: SBI's fixed deposit rates have been reduced by 25 basis points across various tenures. The new rates range from 3.05% to 6.45% for general citizens and 3.55% to 7.05% for senior citizens. - *Fixed Deposit Tenures*: Here are the revised FD interest rates for different tenures: - *211 days to less than 1 year*: 6.05% (general citizens), 6.55% (senior citizens) - *1 year to less than 2 years*: 6.25% (general citizens), 6.75% (senior citizens) - *2 years to less than 3 years*: 6.45% (general citizens), 6.95% (senior citizens) - *3 years to less than 5 years*: 6.3% (general citizens), 6.8% (senior citizens) - *5 years to up to 10 years*: 6.05% (general citizens), 7.05% (senior citizens) - *Reason for Rate Cut*: The rate cut is aimed at protecting the bank's margins after the RBI's 50 basis points repo rate cut. With around 45% of SBI's loan book linked to the repo rate, the bank's top home loan rates for new customers now stand at 7.5%. - *Impact on Bank's Finances*: The decrease in the benchmark rate is projected to reduce the bank's annual interest income by around Rs 8,100 crore. However, reducing savings deposit rates is expected to save the bank approximately Rs 5,750 crore annually .

*PwC is hiring Directors with Finance Transformation skills in Gurgaon, Mumbai, and Bangalore.* Here's a breakdown of the job requirements and details: *Job Title:* Director - Finance Transformation *Key Responsibilities:* - *Finance Transformation:* - Understand core finance processes like Procure to Pay, Order to Cash, and Record to Report - Familiarity with digital tools, including Core ERP and bolt-on solutions - Knowledge of transformation methodologies and frameworks - Experience with strategy-to-execution transformation programs - Operating model assessment, design, and rollout capabilities - *Leadership and Team Management:* - Lead teams and project workstreams - Support business development activities - Coach and guide project teams - Manage timelines, resources, and project economics *Preferred Skill Sets:* - Experience in GBS offshore and finance transformation - Strong skills in PowerPoint, Excel, and Visio - Experience with process mining is a plus - Solid understanding of technology and business use cases *Eligibility Criteria:* - *Experience:* 12+ years - *Education:* CA/MBA/BE/B.Tech - *Background:* Management consulting background preferred *How to Apply:* Interested candidates can share their resumes with Rashmi R Gupta at [email protected].

*The power of consistency* If you improve by just 1% every day, you won’t be twice as good after a year. You’ll be 38x better. 📈 1.01³⁶⁵ = 37.78 *Small wins add up.*

The Indian government plans to amend the Income Tax Bill 2025 to address a contradictory clause that denies refunds for belated returns. According to officials, this clause was a drafting error, and the refund rules will remain the same as the current law. *Key Points:* - *Section 433*: The new Income Tax Bill 2025 states that a refund must be claimed by filing a return, regardless of whether it's belated. However, Section 263(1)(a)(ix) specifies that to qualify for a refund, the return must be filed on or before the due date, creating a contradiction. - *Amendment*: The government is likely to amend this provision to align with the current law, allowing taxpayers to claim refunds even if they file belated returns. - *Current Refund Process*: Taxpayers can claim refunds by filing their income tax returns and declaring their income, deductions, and tax paid details. Refunds are usually credited to the taxpayer's account within 4 to 5 weeks after e-verification of the return. *Impact on Taxpayers:* - Taxpayers who file belated returns will still be eligible for refunds. - The amendment aims to resolve the confusion caused by the contradictory clause and provide clarity on refund rules .