
Memo Makanika
142 subscribers
About Memo Makanika
MemoMakanika is a female motor mechanic who offers mobile automotive service unit that comes to your house,business or any other premises. I will save you the time and hassle of taking your vehicle to a service centre.
Similar Channels
Swipe to see more
Posts

When you start your engine, it's a good practice to allow it to idle for 30 seconds to 1 minute before driving — especially in colder weather. Here's why: --- Why You Should Let the Engine Idle Briefly: 1. Oil Circulation: It gives time for the engine oil to fully circulate and lubricate all moving parts. 2. Stabilize Engine Speed: The idle period lets the engine control system settle into proper fuel and air mixtures. 3. Temperature Regulation: It begins to gently warm the engine and transmission without putting them under sudden load. 4. Turbocharged Engines (if applicable): In turbo engines, brief idling helps reduce wear during startup and shutdown. --- But Don’t Idle Too Long: Modern engines don’t need long warmups. Excessive idling wastes fuel and increases engine wear. After about a minute, it’s best to drive gently — this warms the engine faster and more efficiently.

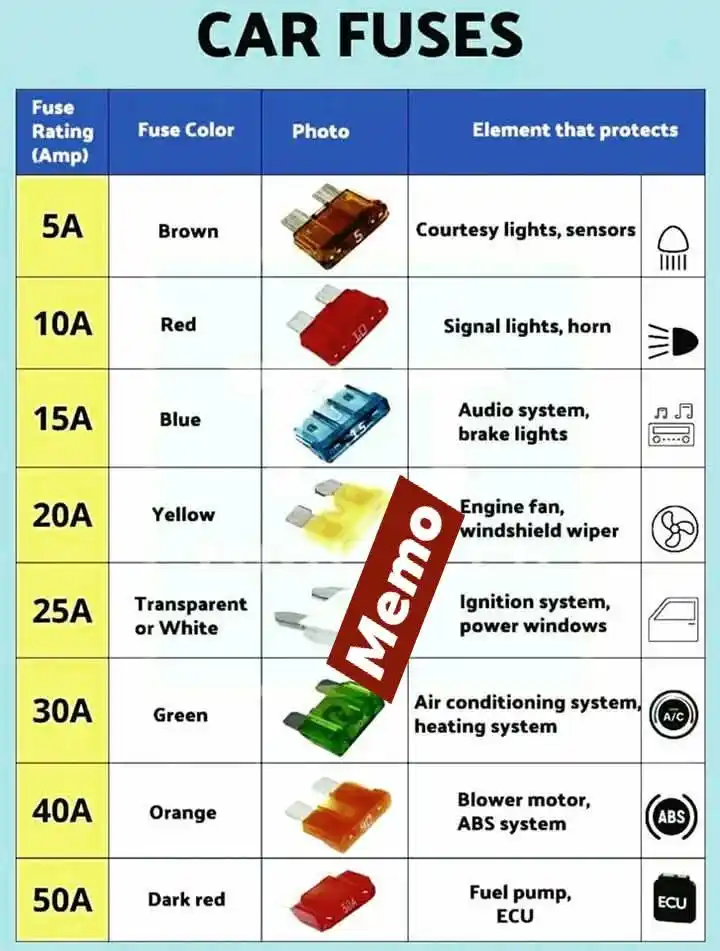
Why You Shouldn't Use the Wrong Fuse Amperage On Your Car!!!! Fuses are like the bodyguards of your car's electrical system . They're there to protect it from overloads and short circuits. But using the wrong fuse amperage can lead to serious trouble: ⏩ Using a Higher Amperage Fuse: 🔹Allows too much current to flow 🔹Can damage wires, sensors, or even start a car fire 🔹The circuit is no longer properly protected! ⏩ Using a Lower Amperage Fuse: 🔹Blows too easily, even under normal load 🔹Causes annoying malfunctions and frequent replacements 🔹Makes the circuit unreliable and unstable ⏩ How to Detect a Bad Fuse!!! Here’s how to check if a fuse has blown: ✅ Step 1: Visual Inspection ▶️Remove the fuse from the fuse box. ▶️Look at the metal strip inside: ▶️ If it's burned or broken, the fuse is bad. ✅ Step 2: Use a Multimeter ▶️Set the multimeter to continuity mode . ▶️Touch the probes to both ends of the fuse: ▶️Beep or low reading = Good fuse ▶️No sound or no continuity = Blown fuse Always replace a blown fuse with the same amperage rating (e.g., replace a 15A fuse with another 15A) Stay safe and protect your car’s electrical system the right way!!!

Does your engine give out blue smoke? It could be this... Oil leak due to valve guide failure 🔧⚠️ When the valve guide wears out or gets damaged, it allows the engine oil to leak into the combustion chamber. This oil burns together with the air-fuel mixture and produces that signature blue smoke that comes out of the exhaust. 🚗💨 What components are involved? 🔹 Valve streak: Part that slides inside the guide. 🔹 Valve Guide: In charge of keeping the stock in line. 🔹 Oil step: Channel through which the lube circulates. 🔹 Combustion chamber: Place where the explosion occurs and... also where the oil shouldn't go! What problems can it cause? ❌ Increased oil consumption ❌ Engine pollution ❌ Combustion failures ❌ Constant blue smoke Solution: Guide and valve seals replacement. Don't ignore it! A small exhaust can cause major damage to the engine. ⚙️

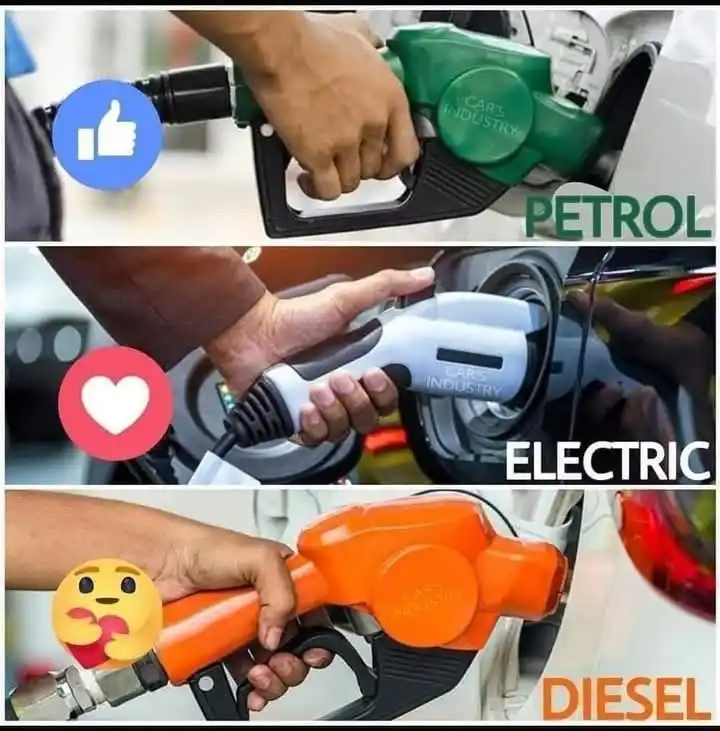
Petrol-powered cars are the most common globally, known for delivering a balance of performance, availability, and relatively lower initial cost. They tend to have quicker throttle response and are favored for smaller, lighter vehicles. However, they burn cleaner than diesel but still contribute heavily to CO₂ emissions, and fuel economy isn’t their strongest trait compared to the alternatives. Electric vehicles are gaining ground fast, offering instant torque, silent operation, and zero tailpipe emissions. With fewer moving parts, they also require less maintenance. The downsides come from limited range, longer charging times compared to refueling, and reliance on charging infrastructure and battery mining, which comes with its own environmental concerns. Still, for city driving and daily use, EVs are becoming the go-to choice in many regions. Diesel engines are torque-heavy workhorses, often used in trucks, SUVs, and long-haul vehicles due to their superior fuel efficiency and pulling power. While they emit less CO₂ than petrol engines, they release more nitrogen oxides and particulates, which have raised concerns over air quality. In recent years, diesel has seen a decline in popularity, especially with tightening emissions regulations and urban restrictions in many parts of the world.


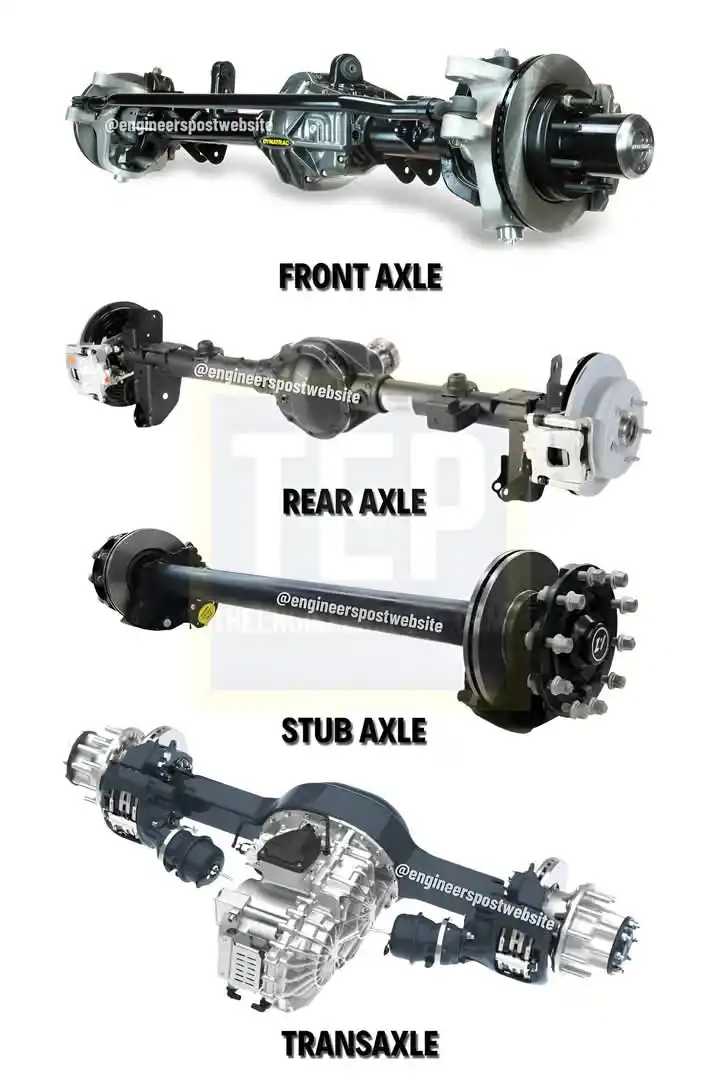
How to Understand Vehicle Axles: Front, Rear, Stub & Transaxle Explained!!! Ever wondered how your car supports its weight, turns smoothly, and delivers power to the wheels? It all comes down to the axles! Let’s break it down: 1️⃣ How to Identify the Front Axle: ⏩ Located at the front ⏩ Supports vehicle weight & enables steering ⏩ Absorbs shocks from the road ⏩ Includes beam, swivel pin, track rod & stub axle ⏩ Usually a dead axle (non-driven) ⏩ In 4WD vehicles, can be a live axle (powered) 2️⃣ How to Spot the Rear Axle: ⏩ Found at the back ⏩ Transfers engine power to the wheels ⏩ Always a live axle (driven) ⏩ Split into two half-shafts linked to a differential Comes in three types: 🔷 Full-floating 🔷 Semi-floating 🔷Three-quarter floating 3️⃣ How to Use a Stub Axle: ⏩ Connected to the front axle via kingpin ⏩ Allows the wheels to pivot with steering 4 Common types: 🔷 Elliot 🔷 Reversed Elliot 🔷 Lamoine 🔷 Reversed Lamoine 4️⃣ How to Understand a Transaxle: ⏩ Combines transmission + differential + axle in one unit ⏩Common in front-wheel-drive & rear-engine vehicles ⏩ Simplifies the drivetrain ⏩ Improves balance & efficiency Know your axles – they’re the backbone of your vehicle's motion!!!!! #Memomakanika


Types of car headlights: 1. Halogen Lights The most popular type of lights on highways these days are halogen lights. They use a combination of gases commonly nitrogen and argon, and tungsten filament in a glass tube. 2. HID Lights Another type of car light that can be used for different lights on a car is the HID light bulb. These HID lights are unique because they don’t have a filament as most light bulbs give. 3. LED Lights These lights are a very energy-efficient kind of headlight that is starting to show up in headlights. These headlights are versatile and bulbs can be made in many different sizes. 4. Laser The most innovative headlight technology currently on the market is laser lighting. For this reason, not only are they the greatest in their class but also the priciest. Laser lights use lasers to ignite a gas. The gas burns incredibly bright as a result. 5. Carbide Carbide headlights were headlights for bicycles and motor cars that used carbide lamps to produce light. 6. Electric Lights Electric headlights, or car headlamps, are lamps that are attached to the front of a vehicle to help drivers see the road at night or in low light conditions.


Driving with low fuel in your car can lead to several potential issues, including: 1. **Fuel Pump Damage**: The fuel pump relies on gasoline for lubrication and cooling. Running low on fuel can cause the pump to overheat and wear out prematurely, leading to costly repairs. 2. **Sediment and Debris**: Over time, sediment can accumulate at the bottom of the fuel tank. When you drive on low fuel, the fuel pump may draw this debris into the engine, which can clog fuel filters and injectors, leading to performance issues. 3. **Increased Risk of Running Out of Gas**: Driving on a low fuel level increases the risk of running out of gas, which can leave you stranded and require roadside assistance. 4. **Fuel Efficiency**: When the fuel level is low, the fuel pump may work harder to draw fuel, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency and performance. 5. **Potential for Engine Misfire**: Low fuel levels can lead to inconsistent fuel delivery, which may cause the engine to misfire or run poorly. 6. **Inconvenience**: Running out of fuel can be inconvenient and time-consuming, as you may need to find a gas station or wait for help. 7. **Safety Concerns**: If you run out of fuel in a dangerous location, such as on a busy highway or in an isolated area, it can pose safety risks to you and your passengers. To avoid these issues, it's generally a good practice to refuel when your tank is about a quarter full. This helps ensure the longevity of your vehicle and reduces the risk of unexpected problems.

The Mystery Behind Water Mixing with Oil in an Engine: Common Causes & Solutions Engines are the heart of any vehicle, operating under extreme pressure, high temperatures, and continuous mechanical stress. Any internal disturbance can escalate into a major issue, one of the most critical being the mixing of water and oil. This unwanted mixture can drastically reduce engine efficiency, damage vital components, and lead to catastrophic failure if left unchecked. Oil and water are not meant to mix inside an engine, except in specific cases like water-cooled turbochargers. When water infiltrates the oil system, it disrupts lubrication, increasing wear and tear on internal parts. Understanding the root causes of this issue is essential for proper maintenance and timely repairs. Not only can this problem lead to expensive fixes, but it may also cause reduced performance, overheating, and even complete engine failure. Let’s explore the most common reasons behind this issue, how to identify symptoms, and what solutions can help fix it! Common Causes of Water Mixing with Oil 1. Worn or Blown Cylinder Head Gasket The cylinder head gasket seals the engine block and cylinder head, keeping oil, coolant, and combustion gases separate. If it fails due to overheating, high mileage, or excessive pressure, coolant can leak into the oil system, creating a milky residue in the oil. Solution: Immediate gasket replacement is necessary to prevent engine failure. 2. Cracked Engine Block A cracked engine block is a serious issue that allows oil and coolant to mix. This can happen due to overheating, manufacturing defects, or physical damage. Symptoms include white smoke from the exhaust, coolant loss, and contaminated oil. Solution: A minor crack might be repairable, but in many cases, the block requires extensive repair or full replacement. 3. Worn Piston Rings Piston rings help seal the combustion chamber and control oil consumption. If they wear out, oil can leak into the coolant passages, causing contamination. This results in reduced engine power, misfires, and oil consumption issues. Solution: Replacing worn piston rings is crucial, but it’s a labor-intensive job requiring partial engine disassembly. 4. Damaged Engine Seals Seals prevent oil and coolant leaks. Over time, heat, contaminants, and wear can damage seals, allowing oil and water to mix. Solution: Replace damaged seals and clean or replace contaminated components to maintain engine performance. 5. Faulty or Improperly Installed Oil Cooler The oil cooler regulates oil temperature by circulating coolant. If the cooler fails or is improperly installed, oil and coolant can cross-contaminate. Solution: Inspect and replace the oil cooler if needed. If it's a new installation, ensure it's properly fitted. 6. Engine Overheating Excessive heat can warp the cylinder head, damage the head gasket, or crack the engine block, creating pathways for coolant to leak into the oil. Solution: Regularly inspect the cooling system, including the radiator, thermostat, and coolant levels, to prevent overheating. 7. Coolant Leak into the Oil System A direct coolant leak can result from damaged seals, worn gaskets, or cracks in the engine block. This leads to oil dilution, reducing its lubrication efficiency and causing increased engine wear. Solution: Check for a milky or frothy appearance in the oil and repair the source of the leak. 8. Condensation Build-Up in the Engine In cold or humid climates, condensation can accumulate in the engine oil when the vehicle is not driven regularly. Over time, this moisture can weaken the oil's lubricating properties. Solution: Drive the vehicle regularly to allow the engine to reach optimal temperature, which helps evaporate moisture. 9. Incorrect Oil or Coolant Mixture Using the wrong type of oil or coolant can lead to contamination and lubrication failure. This can cause overheating and long-term damage. Solution: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil and coolant types to prevent compatibility issues. 10. Engine Oil Cooler Failure The engine oil cooler helps regulate oil temperature using coolant. If it fails, coolant may leak into the oil passages, causing contamination. Solution: Replace the oil cooler and thoroughly flush the engine oil system to remove contamination. Conclusion: Prevention is Key! The mixing of oil and water in an engine is a serious issue that can lead to expensive repairs or complete engine failure if ignored. Whether caused by worn gaskets, overheating, or faulty seals, early detection and repair are crucial. ✅ Regular maintenance ✅ Monitor oil condition & coolant levels ✅ Address overheating issues quickly ✅ Use manufacturer-approved oil & coolant By taking proactive steps, vehicle owners can prevent costly breakdowns, while mechanics can ensure accurate diagnoses and effective repairs. With proper care, your engine will continue to run smoothly and efficiently for years to come













