UPSC Economy UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC™
February 24, 2025 at 03:13 PM
🔆 Analysis of India's import tariffs, particularly in comparison to the US and other BRICS nations, highlighting the focus on agricultural protectionism.
Tariff Comparison:
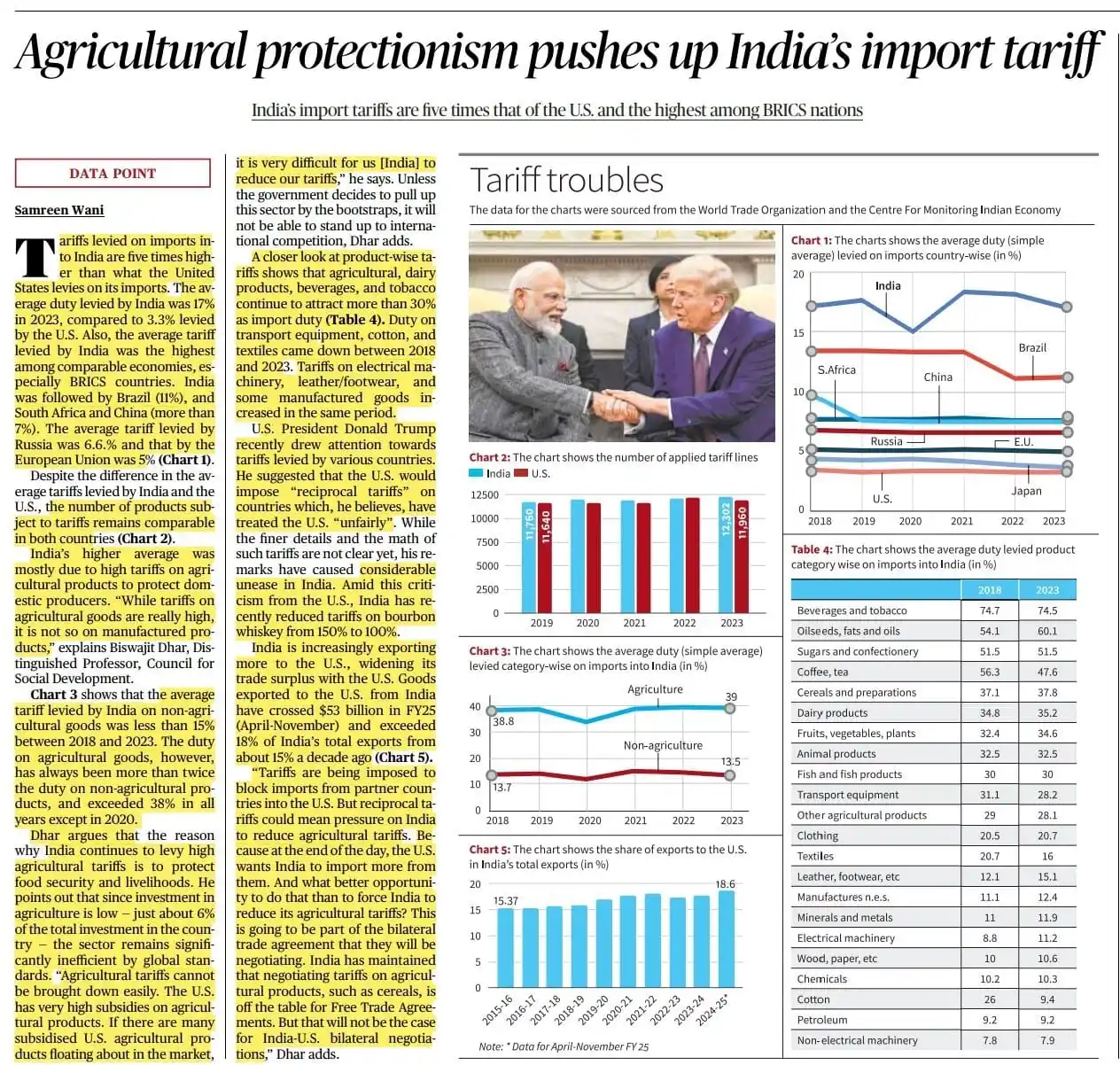
✅India's Average Tariff: 17% (2023), highest among BRICS, five times higher than US (3.3%).
🔸BRICS: Brazil (11%), South Africa & China (>7%), Russia (6.6%).
🔸EU: 5%.
✅Product Coverage: Comparable number of tariff lines between India and US.
Agricultural Tariffs:
🔸High Tariffs: >30% on agricultural, dairy, beverages, tobacco.
🔸Protectionism: Aims to protect domestic producers, food security, livelihoods.
✅Non-Agricultural Tariffs: <15% (2018-2023).
🔸US Subsidies: High US agricultural subsidies make tariff reduction difficult for India.
Trade Dynamics:
✅India-US Trade Surplus: India's exports to US increased to >$53 billion (FY25), 18% of total exports.
✅Potential US Pressure: Reciprocal tariffs could force India to reduce agricultural tariffs.
✅Bilateral Negotiations: Agricultural tariffs likely part of India-US trade agreement talks.
✅India's Stance: Resistant to negotiating agricultural tariffs in Free Trade Agreements.
Product-Wise Tariff Changes (2018-2023):
🔸Decreased: Transport equipment, cotton, textiles.
🔸Increased: Electrical machinery, leather/footwear, some manufactured goods.
Possible Questions:
✅Prelims: Which of the following statements regarding India's import tariffs is/are correct?
India's average import tariff is the highest among BRICS nations.
Agricultural products attract significantly higher tariffs compared to non-agricultural goods.
The number of products subject to tariffs is significantly higher in India compared to the US.
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
✅Mains: "India's agricultural protectionism, while crucial for safeguarding domestic livelihoods, poses a challenge in its trade negotiations with the US." Discuss this statement, highlighting the economic and political factors influencing India's tariff policies and suggesting a way forward that balances domestic interests with international trade dynamics.