
JAMA Network
May 12, 2025 at 08:50 PM
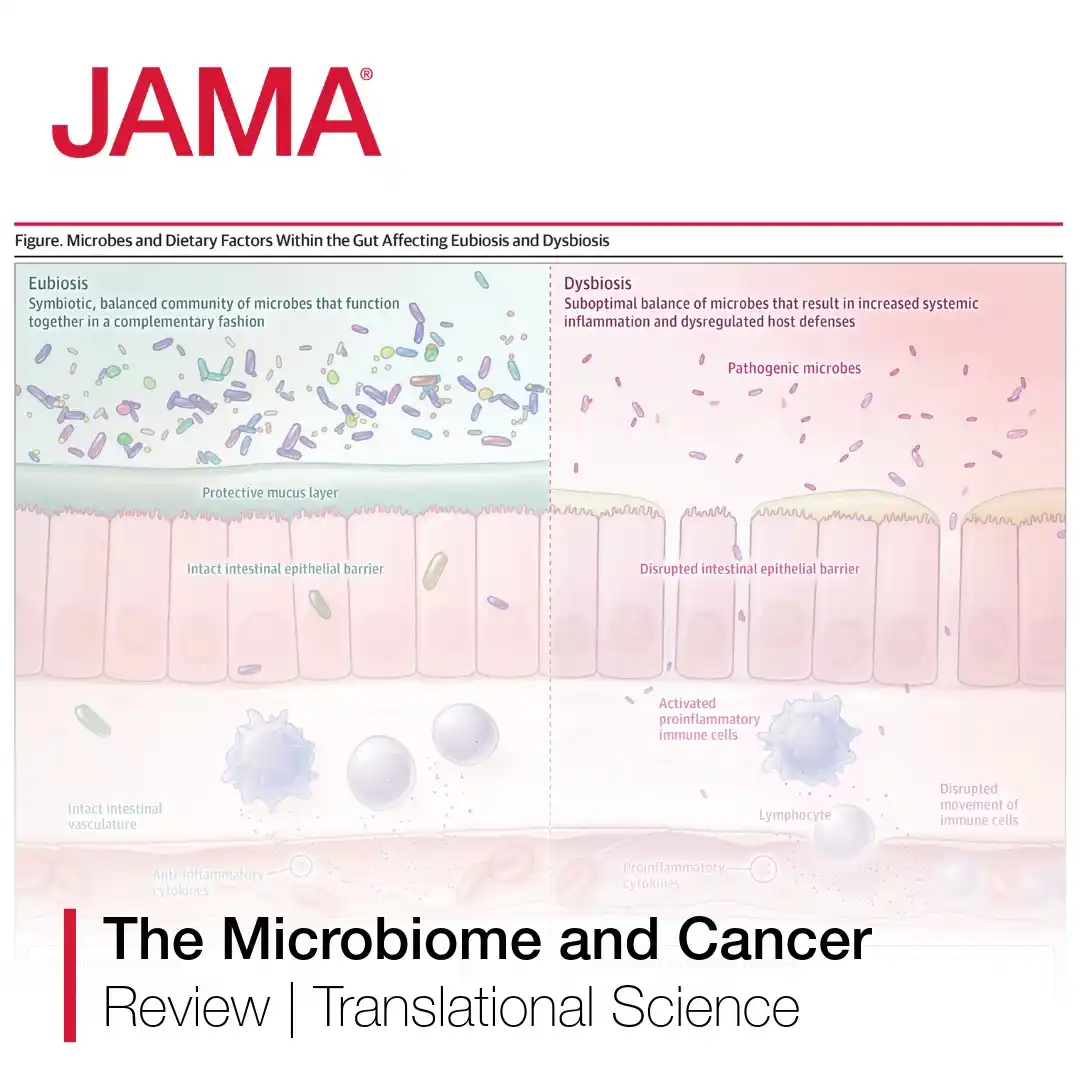
Growing evidence suggests that microbes located within the gastrointestinal tract and other anatomical locations influence the development and progression of diseases.
Microbes indirectly affect human health and disease by influencing immunity, metabolism, and mucosal barrier maintenance. Variations in the microbiome, inside and outside of the gut, have been linked to response to cancer treatment, treatment-related adverse effects, and long-term outcomes in patients with cancer.
➡️ Learn more about the current evidence regarding the human microbiome and cancer in this JAMA Review: ja.ma/3YDdMgf
❤️
👍
😮
13