UPSC Polity UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC™ UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC UPSC™
June 12, 2025 at 02:10 PM
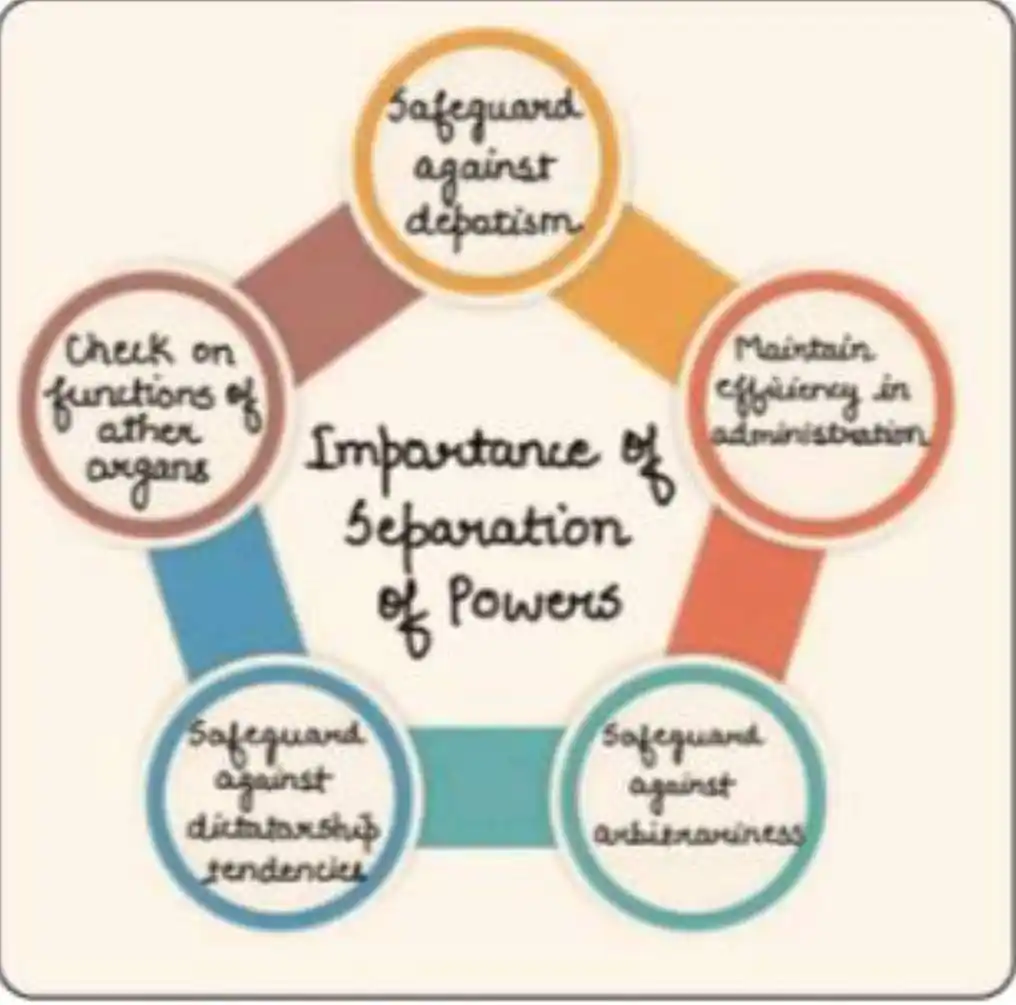
🔆 Constitutional Provisions on Separation of Powers
📍 Key Provisions Ensuring Balance Among Organs
✅ Article 50: Directs the State to separate judiciary from the executive, especially in lower courts.
✅ Part V & Part VI: Clearly define roles of Executive, Legislature, and Judiciary at Union and State levels.
✅ Articles 121 & 211: Prohibit Parliament/State Legislatures from discussing conduct of Supreme Court or High Court judges in their official duties.
✅ Articles 122 & 212: Prevent judiciary from questioning legislative procedures—upholding legislative privilege.
📍 Structural Safeguards
✅ Office of Profit: Limits legislators from holding executive posts, though exceptions exist in India’s parliamentary system.
✅ 91st Amendment: Caps the Council of Ministers to 15% of legislature strength, minimizing executive-legislature fusion.
✅ Article 98: Empowers Parliament to manage its own secretariat and staffing, separate from executive control.
✅ Article 146: Grants CJI control over Supreme Court staff appointments, unless Parliament legislates otherwise.
📍 Conclusion
✅ These provisions help maintain institutional independence, promote checks and balances, and prevent concentration of power, even in a parliamentary democracy like India.
#gs2