Lois Ala Tutorials
May 22, 2025 at 08:36 PM
*CPR PROCEDURES*
*CPR Procedures: Saving Lives One Beat at a Time*
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving technique that has been practiced for decades. It is an essential skill that can be performed by anyone, regardless of their medical background. CPR procedures involve a series of actions aimed at maintaining blood circulation and providing oxygen to the brain during cardiac arrest or other medical emergencies.
The origins of CPR can be traced back to ancient times when various methods were used to revive unconscious individuals.
However, it was not until the 1960s that modern CPR techniques were developed and standardized. Dr. James Jude, Dr. Peter Safar, and Dr. William Kouwenhoven are credited with pioneering these life-saving procedures.
CPR is crucial because it buys time for professional medical help to arrive while sustaining vital organ functions in the meantime.
When someone experiences cardiac arrest, their heart stops beating effectively, depriving the brain and other organs of oxygen-rich blood. By performing CPR immediately after cardiac arrest occurs, bystanders can significantly increase the chances of survival.
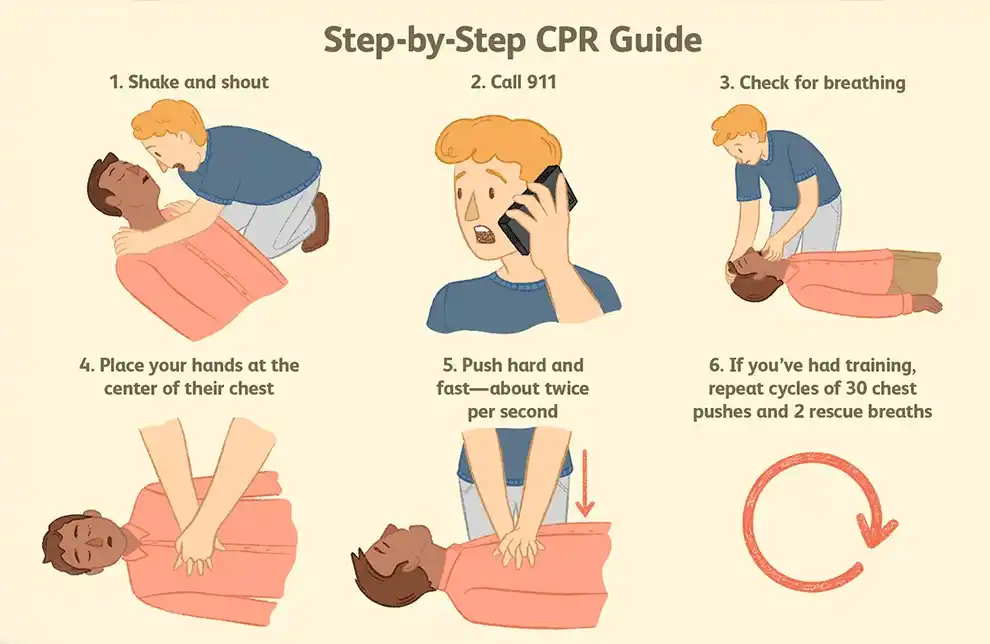
The first step in performing CPR is assessing the situation for safety hazards and determining if the person is responsive or not breathing normally. If there are no immediate dangers present and the person is unresponsive or not breathing normally, it is crucial to call emergency services right away.
Once emergency services have been contacted, chest compressions should be initiated immediately on an adult victim who does not have a pulse or is not breathing normally.
*To perform chest compressions correctly:*
1) Place one hand on top of the other in the center of the victim's chest.
2) Position yourself directly over your hands with your shoulders aligned above your hands.
3) Push hard and fast at least two inches deep into their chest at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
4) Allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions.
It is important to note that the depth and speed of compressions are critical for effective CPR. The force applied during compressions should be sufficient to adequately circulate blood but not excessive enough to cause injury.
Maintaining a steady rhythm is also crucial, as it ensures proper blood flow and oxygenation.
In addition to chest compressions, rescue breaths are an integral part of CPR procedures. After 30 compressions, the rescuer should deliver two rescue breaths by tilting the victim's head back slightly and lifting their chin. This allows for an open airway, enabling effective ventilation.
Each breath should be delivered over one second and result in visible chest rise.
However, if the rescuer is unwilling or unable to provide rescue breaths due to concerns about infectious diseases or other reasons, hands-only CPR can still be performed effectively.
Hands-only CPR involves continuous chest compressions without rescue breaths until professional help arrives.
CPR procedures may vary slightly when performed on infants or children due to their smaller size and different physiological needs.
However, the basic principles remain the same: assess responsiveness, call emergency services, initiate chest compressions with appropriate depth and speed, and provide rescue breaths if possible.
CPR procedures are a vital skill that can save lives in emergency situations such as cardiac arrest. By following a series of steps including assessing responsiveness, calling emergency services immediately, initiating chest compressions with proper technique and speed, and providing rescue breaths if possible – bystanders can significantly increase the chances of survival until professional medical help arrives.
It is essential for individuals from all walks of life to learn these life-saving techniques as they have the potential to make a significant difference in someone's life when every second counts.