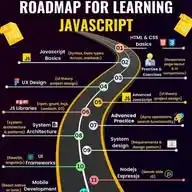
JavaScript
June 18, 2025 at 07:43 AM
*A–Z of JavaScript programming concepts* 🚀
*A – Async/Await*
Handles asynchronous operations in a cleaner way compared to promises.
```js
async function fetchData() {
let response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/data');
let data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
}
```
*B – Browser Events*
Handles user interactions using event listeners like `click`, `keydown`, etc.
```js
document.addEventListener('click', () => console.log('Clicked!'));
```
*C – Closures*
Functions that retain access to their parent scope even after execution.
```js
function outer() {
let count = 0;
return function inner() {
count++;
return count;
};
}
```
*D – DOM (Document Object Model)*
JavaScript interacts with HTML elements through the DOM.
```js
document.getElementById('myDiv').innerText = "Hello!";
```
*E – ES6 (ECMAScript 2015+)*
Major update introducing `let`, `const`, arrow functions, template literals, etc.
*F – Fetch API*
Modern way to handle HTTP requests instead of `XMLHttpRequest`.
```js
fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
```
*G – Generators*
Functions that yield multiple values lazily.
```js
function* generateNumbers() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
}
```
*H – Hoisting*
JavaScript moves declarations to the top during execution.
```js
console.log(a); // Undefined (not an error)
var a = 10;
```
*I – Immediately Invoked Function Expressions (IIFE)*
Functions that execute immediately after definition.
```js
(function () { console.log('IIFE runs instantly!');})();
```
*J – JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)*
Lightweight data format widely used in APIs.
```js
const jsonData = '{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}';
const obj = JSON.parse(jsonData);
```
*K – Key-Value Pairs (Objects)*
Objects store data in key-value format.
```js
const user = { name: "John", age: 25};
```
*L – Lexical Scope*
Variables are accessible within the scope they’re declared.
*M – Map Object*
Stores key-value pairs but allows object keys as well.
```js
const map = new Map();
map.set('name', 'Alice');
```
*N – Null vs Undefined*
`null` is an intentional absence of value, while `undefined` means uninitialized.
*O – Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)*
Supports class-based or prototype-based inheritance.
```js
class Car {
constructor(model) {
this.model = model;
}
}
```
*P – Promises*
Handles asynchronous operations cleanly.
```js
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve("Success!");});
```
*Q – Query Selector*
Easily selects elements in the DOM.
```js
document.querySelector('.myClass');
```
*R – Reduce Method*
Processes array values into a single result.
```js
const nums = [1, 2, 3];
const sum = nums.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0);
```
*S – Spread & Rest Operators*
Expands or collects values in arrays or objects.
```js
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = [...arr1, 4, 5]; // Spread
function sum(...numbers) { return numbers.reduce((a, b) => a + b);} // Rest
```
*T – Ternary Operator*
Shortens `if-else` statements.
```js
const result = age> 18? "Adult": "Minor";
```
*U – Use Strict Mode*
Helps write cleaner JavaScript.
```js
'use strict';
```
*V – Variables (`var`, `let`, `const`)*
Modern JavaScript favors `let` and `const` over `var`.
*W – Web APIs*
JavaScript can access browser features like *Local Storage*, *Canvas*, and *Geolocation*.
*X – XMLHTTPRequest*
Older method for making HTTP requests before `fetch()`.
*Y – Yield (Generators)*
Pauses function execution until `next()` is called.
*Z – Zero-Based Indexing*
Arrays start indexing from zero.
💬 *React ❤️ if this was helpful!*🚀
❤️
👍
♥
🇨🇲
🙏
🇪🇬
🇬🇭
🇳🇬
🎉
😅
36