Aviator Fady
June 13, 2025 at 10:31 AM
✈️ ICAO Annex 16 – Volume II: Aircraft Engine Emissions
Title: Environmental Protection – Aircraft Engine Emissions
Objective:
To limit and control emissions from aircraft engines that impact local air quality and contribute to climate change.
🔹 Key Components
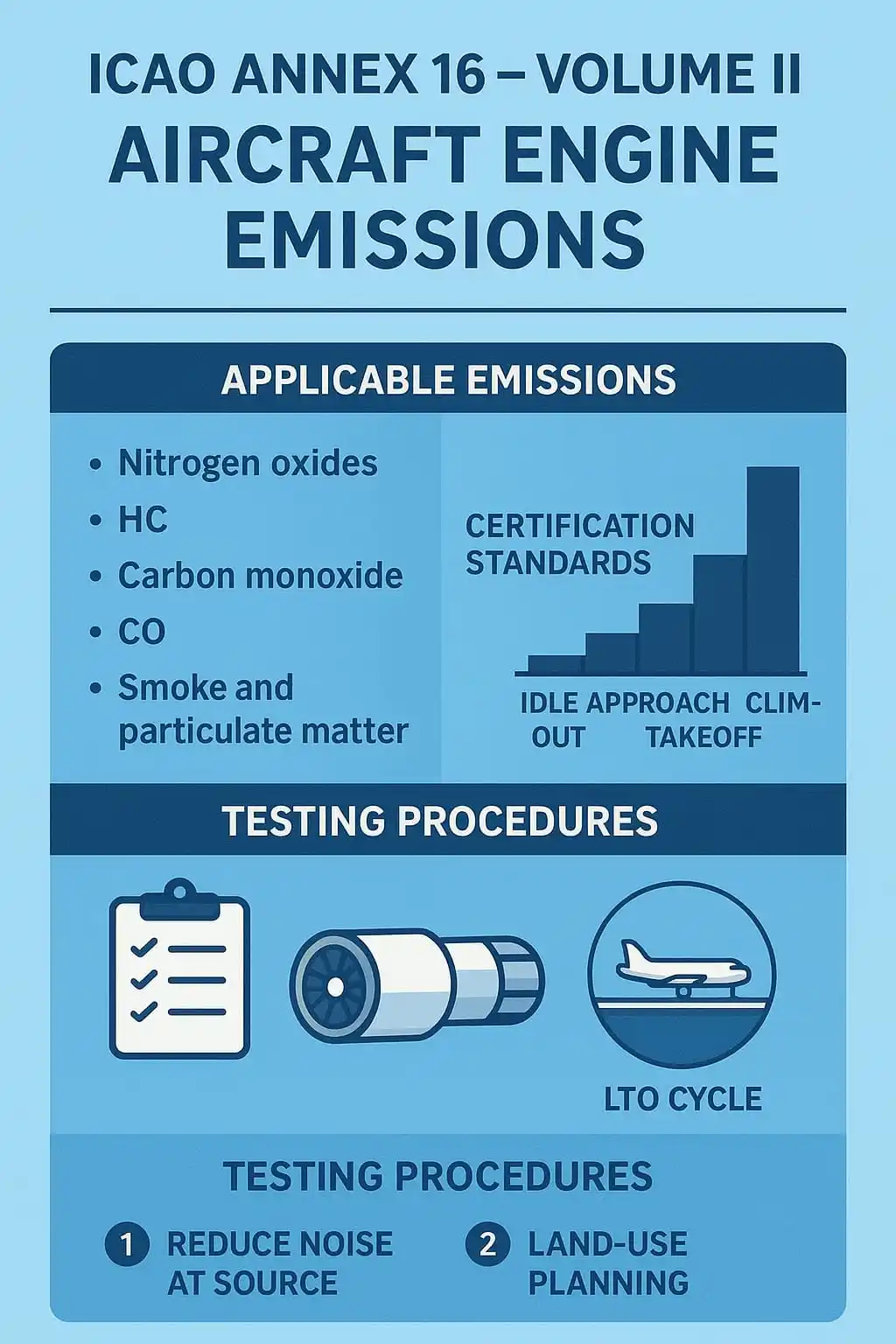
1. Applicable Emissions
Focuses on emissions from turbojet and turbofan engines with thrust > 26.7 kN, specifically:
▪️Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ)
▪️Hydrocarbons (HC)
▪️Carbon monoxide (CO)
▪️Smoke and particulate matter (PM)
2. Certification Standards
Emissions are tested during four operating modes:
▪️Idle
▪️Approach
▪️Climb-out
▪️Takeoff
Results are compared to ICAO’s regulatory emission limits.
3. Testing Procedures
▪️Engine emissions are measured under controlled conditions (test benches).
Standardized using:
▪️Landing and Takeoff (LTO) Cycle: Represents emissions near airports (up to ~3,000 ft).
▪️Prescribed engine settings, fuel flow, and ambient conditions.
4. Smoke & Particulates
▪️Limits on visible smoke are enforced for aesthetic and pollution concerns.
▪️Newer standards also address non-volatile particulate matter (nvPM).
5. Applicability
▪️Applies to new engine types and sometimes retroactively to older models under recertification.
▪️Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance for each engine model.
🌍 Environmental Impact
☢️Pollutant ▶️Effect
☢️NOₓ ▶️Contributes to ozone formation & acid rain
☢️CO ▶️Toxic gas, harmful to health
☢️HC▶️ Contributes to smog and ozone
☢️Smoke/nvPM ▶️Reduces visibility, harms respiratory health