Code EM - Emergency Medicine / Medical Update
516 subscribers
About Code EM - Emergency Medicine / Medical Update
Stay updated with the latest research, clinical pearls, and interesting topics in emergency medicine. Embrace your inner nerd and dive into the world of EM! 🖋️Dr Joemon Sujo Emergency Medicine Resident, GMC Trivandrum https://wa.me/919495355095 #emergencymedicine #emeducation #nerdalert #medicaleducation #ebm I will do my level best to varify the authenticity of every post, if you find any mistakes or improvement to made in any post please give me the feed back I'll make the change with pleasure
Similar Channels
Swipe to see more
Posts

https://youtu.be/MP_zOb8pNOg?si=6MlEKIm4EUYUYM2Z

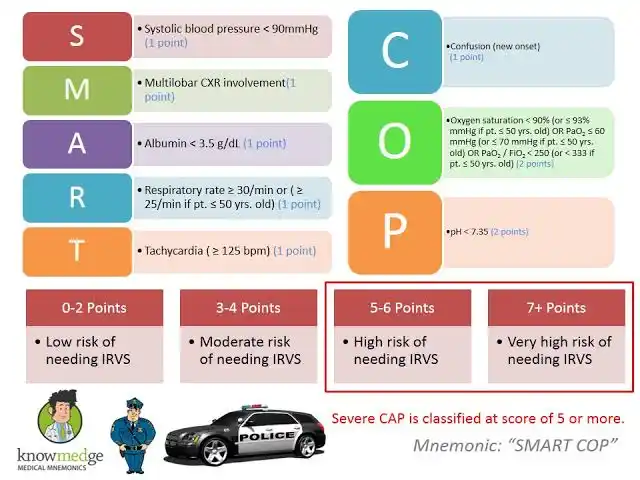
*SMART-COP Score* https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.27248 The SMART-COP score *assesses the severity* of community-acquired pneumonia *(CAP)* and predicts the need for intensive respiratory or vasopressor support (IRVS). - A score of ≥3 points identifies approximately 92% of patients requiring IRVS, including 84% of those not needing immediate ICU admission. The score is particularly useful in emergency settings to guide decisions on hospital admission, ICU care, or outpatient *# Limitations* - May underestimate severity in specific populations (e.g., tropical regions). - Should be used alongside clinical judgment, not as a sole decision-making tool. - Less effective for predicting mortality compared to other scores like PSI or CURB-65. https://litfl.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/etg-smartcop.pdf

Initial Testing Bundle: - Order HBsAg, anti-HBc, and anti-HBs Then follow the HBsAg result: *1. If HBsAg is Positive* : - Order IgM anti-HBc - If IgM anti-HBc is positive → _Acute HBV Infection_ - If IgM anti-HBc is negative → _Chronic HBV Infection_ - For chronic infection, order additional tests: * HBeAg * HBV DNA * LFTs (Liver Function Tests) * Liver fibrosis assessment *2. If HBsAg is Negative:* Check anti-HBc status: A. If anti-HBc is Positive: - Check anti-HBs - If anti-HBs positive → _Resolved HBV Infection_ - If anti-HBs negative → _Four possible interpretations:_ 1. _Resolved infection_ 2. _False positive anti-HBc_ 3. _'Low level' chronic infection_ 4. _Window period_ B. If anti-HBc is Negative: - Check anti-HBs - If anti-HBs positive → _Immune due to vaccination_ - If anti-HBs negative → _Susceptible (candidate for vaccination)_ This systematic approach helps determine the patient's Hepatitis B status and appropriate next steps in management.

Would like to suggest a nice you tube channel for EBM fans here https://youtube.com/@first10em?si=YLzHDJtlCGNQ7QmS Evidence based medicine is the perk of modern medicine this channel is nice in giving you monthly update as BroomeDocs podcast https://youtu.be/nVxgLZv7xIw?si=Bo-4UuaH17V5adi1 Occasion discussion on clinical scenarios Link to few of my favorite discussion Status epilepsy https://youtu.be/wmbF9wH678s?si=XBdrxaVezmwcrBun SVT https://youtu.be/HHwguwoqzjY?si=yEHKR9-x4EinZdnv RSI vs DSI https://youtu.be/5g4cV1JaIZQ?si=aaW8pEkHT7pqD7mY

*Cardiogenic shock may be roughly conceptualized as requiring two components:* (1) Systemic hypoperfusion due to low cardiac output (cold).❄️ (2) Filling pressures are elevated due to fluid overload (wet)💧 🥲Giving volume will worsen their pulmonary congestion (making them wetter). 🥲Removing volume will worsen their systemic hypoperfusion (making them colder). Management of cardiogenic shock usually requires interventions to improve cardiac function (e.g., inotropic medications, revascularization, or a mechanical support). Cardiogenic shock patients may look deceptively OK, but they are indeed critically ill. Early recognition facilitates appropriate ICU management. The patient with unrecognized cardiogenic shock will generally fail to respond to non-intensive therapy, running in circles (typically the patient is initially diuresed, then develops worsening renal failure, then is given fluid back, then develops pulmonary edema, then transferred to ICU). https://emcrit.org/ibcc/chf/#bedside_hemodynamic_assessment

*New Scientific Statement from AHA: Management of Elevated Blood Pressure in Acute Care Settings* *Hypertensive Emergency:* SBP/DBP >180/110-120 mmHg + target-organ damage *Asymptomatic Markedly Elevated BP:* SBP/DBP >180/110-120 mmHg (formerly "hypertensive Urgency") with out end-organ damage *Asymptomatic Elevated BP:* SBP/DBP ≥130/80 mmHg No more recommendation for previous terms ❌ *Hypertensive criss* SBP/DBP > 180/110 irrespective of end-organ status ❌ *Accelerated hypertension* - SBP/DBP > 180/110 with neuroretinal - hemorrhagic spots or exudate in fundoscopy ❌ *Malignant hypertension* - SBP/DBP > 180/110 with papillary edema in fundoscopy ❌ *Hypertensive Urgency* 🔁 *Asymptomatic Markedly Elevated BP* ✅ 🆕 *Asymptomatic Elevated BP* ✅

Dose of hydrocortisone in sepsis shock Inj Hydrocortisone 50mg IV Q6h