Welding Fabrication World
February 23, 2025 at 05:32 PM
1d
𝐇𝐚𝐫𝐝𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐓𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐨𝐟 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐚𝐢𝐫 𝐖𝐞𝐥𝐝𝐬 (𝐀𝐬 𝐩𝐞𝐫 𝐀𝐏𝐈 𝟓𝟕𝟕)
Hardness testing helps ensure weld integrity, prevents failures, and maintains compliance with industry standards like API 582 and NACE SP0472. Here’s what you need to know about on-site hardness testing of repair welds:
1️⃣ When is Hardness Testing Required?
• Conducted after PWHT to check for excessive hardness, which may lead to brittle failures.
• Required for repair welds, using portable hardness testers as per ASTM A833, ASTM A1038, or ASTM A956.
2️⃣ How is Hardness Testing Performed?
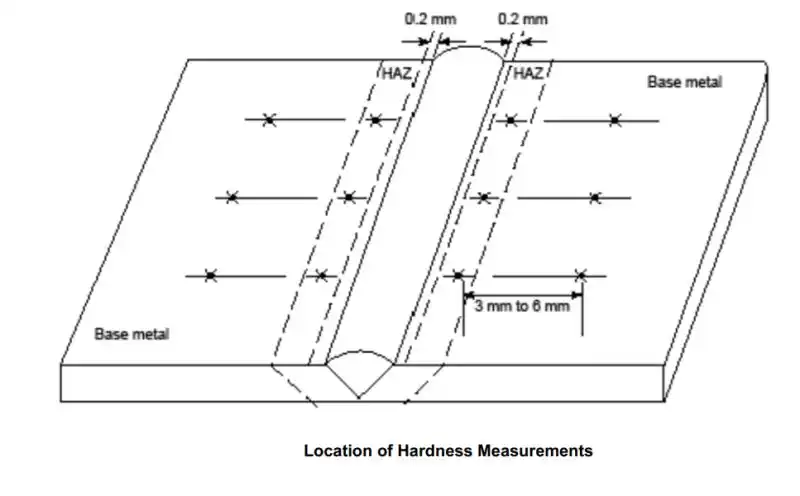
• Hardness measurements are taken in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), as close as 0.2 mm to the weld interface.
• The surface must be polished to a roughness of 0.4 μm (16 μin.) max before testing.
• Etching is done to clearly identify the weld metal, weld interface, and HAZ.
3️⃣ Test Procedure and Variability
• Typically, five impressions in a 1 in² (650 mm²) area make up a single hardness test.
• Field hardness testing may show variability due to surface conditions, equipment type, and operator technique.
• Additional verification through Field Metallography Replication (FMR) can help assess HAZ microstructure and confirm results.
Figure shows hardness measurement locations.
#hardnesstesting #weldinspection #pwht #ndt #weldingquality #engineering #pressurevessels #metallurgy
diagram, engineering drawing